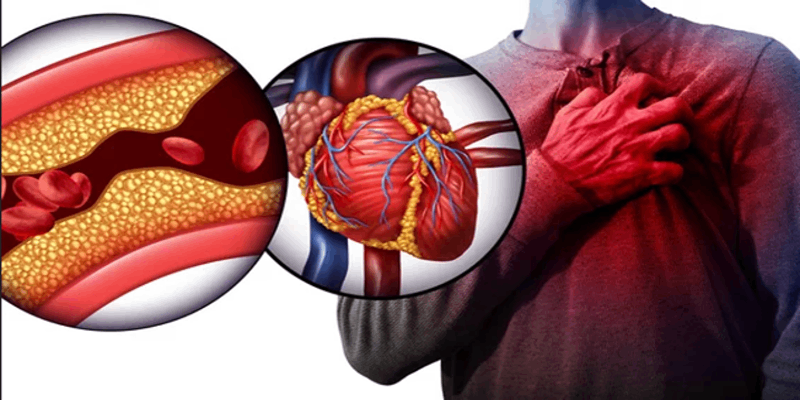
Heart Diseases
Heart diseases, also known as cardiovascular diseases (CVDs), are a group of disorders that affect the heart and blood vessels. These diseases are among the leading causes of death globally and can significantly impact a person's quality of life.
Types of Heart Diseases:
- Coronary Artery Disease (CAD): This is the most common type of heart disease and occurs when the arteries that supply blood to the heart muscle become narrowed or blocked due to plaque buildup (atherosclerosis). CAD can lead to chest pain (angina), heart attacks, and other complications.
- Heart Attack (Myocardial Infarction): A heart attack occurs when blood flow to a part of the heart is blocked, usually by a blood clot, causing damage to the heart muscle. It is often a result of CAD.
- Heart Failure: Also known as congestive heart failure, this condition occurs when the heart is unable to pump blood effectively to meet the body's needs. It can result from various conditions, including CAD, high blood pressure, or previous heart attacks.
- Arrhythmias: These are irregular heartbeats that can be too fast, too slow, or erratic. Common types include atrial fibrillation, bradycardia, and ventricular tachycardia. Some arrhythmias are harmless, but others can be life-threatening.
- Valvular Heart Disease: This involves damage to or a defect in one of the four heart valves, which control the flow of blood through the heart. Conditions like valve stenosis (narrowing) or regurgitation (leakage) can lead to heart problems.
- Cardiomyopathy: This refers to diseases of the heart muscle, where the heart becomes enlarged, thickened, or stiffened, affecting its ability to pump blood. Cardiomyopathy can be genetic or caused by other conditions.
- Congenital Heart Disease: These are heart defects present at birth, such as holes in the heart, abnormal heart valves, or improper connections between blood vessels.
- Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD): This occurs when the arteries in the legs or arms are narrowed or blocked, reducing blood flow to these areas. PAD is similar to CAD but affects the limbs rather than the heart.
- Aortic Aneurysm: This is a bulge in the wall of the aorta, the main artery that carries blood from the heart to the rest of the body. If an aneurysm ruptures, it can be life-threatening.
Causes and Risk Factors:
- Unhealthy Lifestyle: Poor diet, lack of physical activity, smoking, and excessive alcohol consumption can contribute to the development of heart diseases.
- High Blood Pressure: Hypertension can damage the arteries, making them more susceptible to narrowing and blockages.
- High Cholesterol: Elevated levels of LDL ("bad") cholesterol can lead to plaque buildup in the arteries.
- Diabetes: Diabetes increases the risk of heart disease by contributing to atherosclerosis and other complications.
- Genetics: A family history of heart disease can increase the risk of developing similar conditions.
- Age and Gender: Risk increases with age, and men are generally at higher risk at a younger age than women, though women's risk increases after menopause.
- Stress and Mental Health: Chronic stress, depression, and anxiety can contribute to heart disease.
Symptoms of Heart Diseases:
- Chest pain or discomfort (angina)
- Shortness of breath
- Fatigue
- Palpitations or irregular heartbeats
- Swelling in the legs, ankles, or feet (edema)
- Dizziness or fainting

